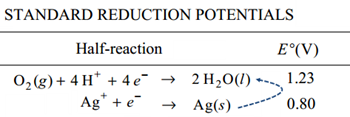AP16 Electrochemistry
Black to move Double check! Rg8+
Check with the AP Coordinator at your host school to confirm that an exam will be waiting for you on the testing date.
March 14, 2025 is the dealine for test site coordinators to order AP exams.

Your brain produces its electric currents via movements of ions. Each nerve cell can produce a voltage (around 70 mV) through differences in ion concentrations. Your thoughts are electrochemical reactions learning about electrochemical reactions.

Chapter 19- the last Chapter
![]() AP16 C19 Electrochemistry Summary
AP16 C19 Electrochemistry Summary
![]() Chapter19 Electrochem Textbook Condensed
Chapter19 Electrochem Textbook Condensed
|
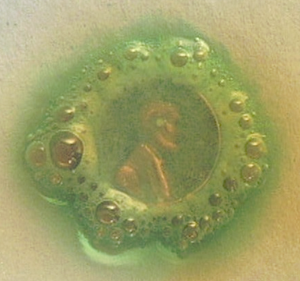
At high temperatures, the copper reacts with oxygen to
Hydrogen can react with the oxygen in copper oxide
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
You should watch this carefully and understand it! The particulate model is excellent. |
 |
|
 |
Electrolysis of water |
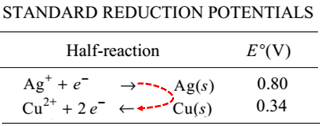
Voltaic Cellsvoltages only involve addition and subtraction, but deciding on which
standard voltage to add or subtract can be confusing.
Rob does a very nice job of sorting this out. It's worth watching.

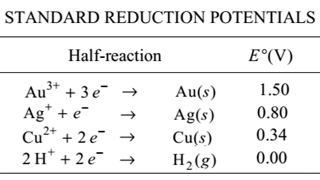
 AP16.15 C19 Galvanic Cells
AP16.15 C19 Galvanic Cells AP16.20 C19 Electrolytic Cells
AP16.20 C19 Electrolytic Cells

The last exam of the semester on AP15 and AP16 will be next week.

Posted labs are due at the end of March.